- Published on
React-beautiful-dnd table row shrinks when dragging
- Reading time
- 3 分钟
- Page view
- -
- Author

- Name
- Yicong
- Github
Recently, I encountered a problem when using react-beautiful-dnd to develop table drag and sort: when a row is selected and dragging begins, the style of the row or cell changes, which is specifically manifested as the width of the entire row shrinks. After searching for information and reading documents, I found a solution to this problem.
Let's take a look at what happens when you drag a row of a standard table. You can see that the dragged row shrinks, which is actually because the column width is lost.
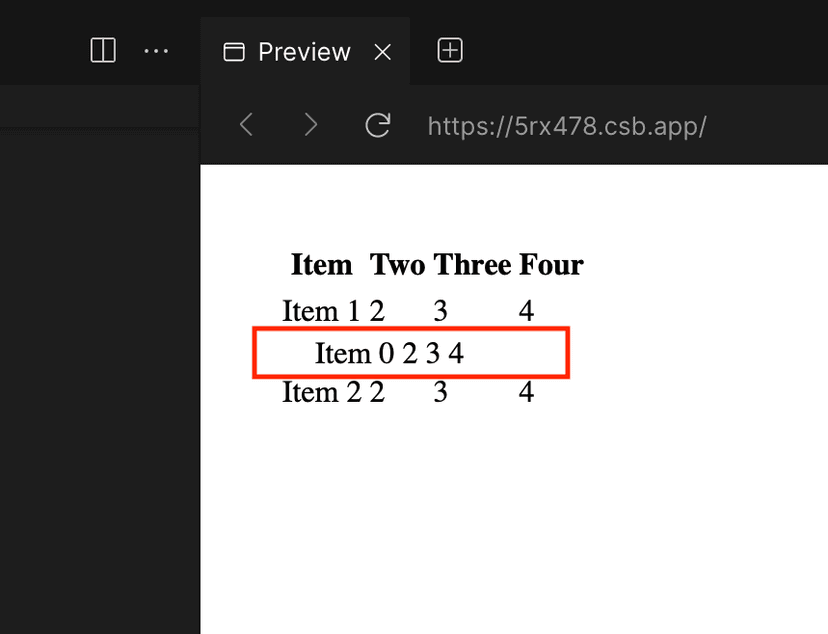
The official documentation of react-beautiful-dnd mentions the method used in the table: Tables. It mentions that two strategies can be used to drag and sort the table, namely Fixed layouts and Dimension locking. Next, I will introduce them respectively.
Fixed layouts
Compared to the latter, Fixed layouts has better performance and is easier to implement, but it is only applicable when the table column width is fixed. In this case, you only need to set display: table for the row wrapped by <Draggable />.
If the above method does not work, you can also directly set a fixed width for the <td> element. For example, here the width of the <td> element is set to 120px:
<DragDropContext onDragEnd={this.onDragEnd}>
<Droppable droppableId="droppable">
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<table
ref={provided.innerRef}
style={getListStyle(snapshot.isDraggingOver)}
>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Title</th>
<th>Test</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{this.state.items.map((item, index) => (
<Draggable key={item.id} draggableId={item.id} index={index}>
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<tr
ref={provided.innerRef}
{...provided.draggableProps}
{...provided.dragHandleProps}
style={getItemStyle(
snapshot.isDragging,
provided.draggableProps.style
)}
>
<td style={{ width: "120px" }}>{item.content}</td>
<td style={{ width: "120px" }}>{item.test}</td>
</tr>
)}
</Draggable>
))}
{provided.placeholder}
</tbody>
</table>
)}
</Droppable>
</DragDropContext>
Of course, this is not the focus of this article. After all, not every table can fix the column width. In many cases, the column width will adapt according to the content in the cell. In this case, the following method can only be used.
Dimension locking
As mentioned earlier, this method is suitable for the case where the column width adapts to the content. Not only that, it is also suitable for the case where the column width is fixed, and it is more robust, but the performance will be relatively poor. When using this method, it is best not to exceed 50 rows of table content. Even if performance is not considered, the dragging experience of hundreds of rows of content will not be very good.
The implementation idea of this method is simply: record the original width and height of each cell of the dragged row before dragging, set the width and height of the cell of the row to the recorded value during dragging, and remove the style after the dragging is completed.
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef } from "react";
import { DragDropContext, Droppable, Draggable } from "react-beautiful-dnd";
class LockedCell extends React.Component {
ref;
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps) {
if (!this.ref) {
return null;
}
const isDragStarting =
this.props.isDragOccurring && !prevProps.isDragOccurring;
if (!isDragStarting) {
return null;
}
const { width, height } = this.ref.getBoundingClientRect();
const snapshot = {
width,
height,
};
return snapshot;
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState, snapshot) {
const ref = this.ref;
if (!ref) {
return;
}
if (snapshot) {
if (ref.style.width === snapshot.width) {
return;
}
ref.style.width = `${snapshot.width}px`;
ref.style.height = `${snapshot.height}px`;
return;
}
if (this.props.isDragOccurring) {
return;
}
// inline styles not applied
if (ref.style.width == null) {
return;
}
// no snapshot and drag is finished - clear the inline styles
ref.style.removeProperty("height");
ref.style.removeProperty("width");
}
setRef = (ref) => {
this.ref = ref;
};
render() {
return (
<td ref={this.setRef} style={{ boxSizing: "border-box" }}>
{this.props.children}
</td>
);
}
}
const App = () => {
const [items, setItems] = useState([]);
const [isDragging, setIsDragging] = useState(false);
// 构造测试数据
const getItems = (count) =>
Array.from({ length: count }, (v, k) => k).map((k) => ({
id: `item-${k}`,
content: `Item ${k}`,
}));
useEffect(() => {
setItems(getItems(3));
}, []);
const onDragEnd = (result) => {
setIsDragging(false);
};
const onBeforeDragStart = () => {
setIsDragging(true);
};
return (
<div style={{ padding: "2rem" }}>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Item</th>
<th>Two</th>
<th>Three</th>
<th>Four</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<DragDropContext
onDragEnd={onDragEnd}
onBeforeDragStart={onBeforeDragStart} // DIMENSION LOCKING
>
<Droppable droppableId="droppable">
{(provided) => (
<tbody {...provided.droppableProps} ref={provided.innerRef}>
{items.map((item, index) => (
<Draggable key={item.id} draggableId={item.id} index={index}>
{(provided, snapshot) => (
<tr
ref={provided.innerRef}
{...provided.draggableProps}
{...provided.dragHandleProps}
>
<LockedCell
isDragOccurring={isDragging}
snapshot={snapshot}
>
{item.content}
</LockedCell>
<LockedCell
isDragOccurring={isDragging}
snapshot={snapshot}
>
2
</LockedCell>
<LockedCell
isDragOccurring={isDragging}
snapshot={snapshot}
>
3
</LockedCell>
<LockedCell
isDragOccurring={isDragging}
snapshot={snapshot}
>
4
</LockedCell>
</tr>
)}
</Draggable>
))}
{provided.placeholder}
</tbody>
)}
</Droppable>
</DragDropContext>
</table>
</div>
);
};
export default App;
It can be seen that the implementation of the drag container has not changed much. The key point is to use <LockedCell> instead of <td>. What does <LockedCell> do specifically?
I have just roughly described it. Use onBeforeDragStart to detect the critical point of the drag state, record the width and height of all cells in the row before dragging, set the width and height to the recorded values during dragging, and clear the style after the drag ends. This is also the reason why this method has low performance, and it needs to frequently read the attributes of DOM elements and render them.